THE CLIMATE-PIMA (C-PIMA)
Green infrastructure investment is critical for an inclusive, sustainable, and climate-focused recovery. Green and resilient public investment is an important enabler for a sustainable recovery—it creates jobs, spurs economic growth, addresses climate change, and improves the quality of life. It can also stimulate much needed private sector investment. Attaining the Sustainable Development Goals while getting on track to achieve Paris Agreement goals requires significant infrastructure investment. The economic and social outcomes of this investment depend crucially on the efficiency of public investment management.
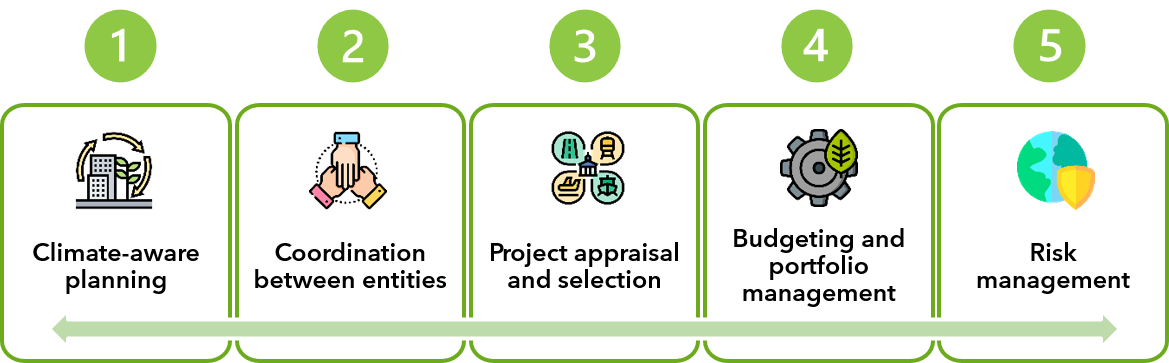
The C-PIMA incorporates climate change in the PIMA framework and assesses countries’ capacity to manage climate-related infrastructure. The C-PIMA is designed around five pillars of public investment management that are key for climate-aware infrastructure: planning, coordination across government, project appraisal and selection, budgeting and portfolio management, and risk management.
Explore C-PIMA Country Assessments >>
Download the Climate-PIMA Framework >>
Download the Climate-PIMA Questionnaire >>
The framework assesses the five key public investment management practices that are most critical to addressing climate challenges.
1. Provides the context of the linkages between climate change and public infrastructure and climate strategies in a country.
2. Presents a detailed assessment, and formulates a set of recommendations in a form of a roadmap of reform priorities.
(Click on the interactive chart to explore)
Loading...
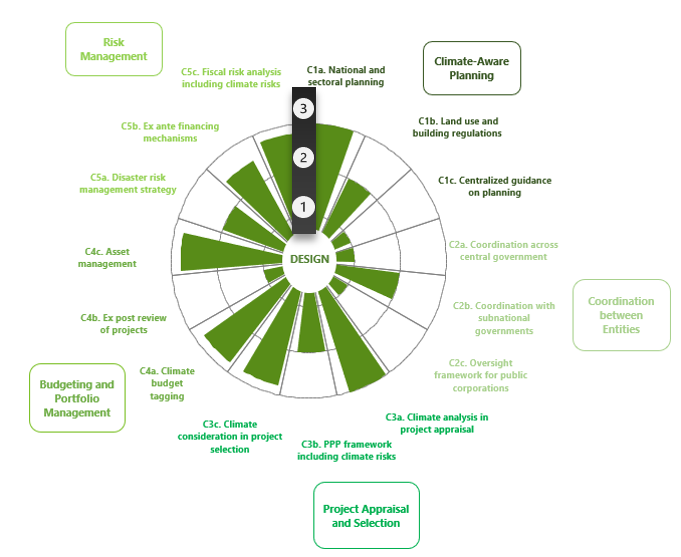
C.1.a.
National and sectoral planning:
Are national and sectoral public investment strategies and plans consistent with NDC or other overarching climate change strategy on mitigation and adaptation?
C.1.b.
Land use and building regulations:
Do central government and/or sub-national government regulations on spatial and urban planning, and construction address climate-related risks and impacts on public investment?
C.1.c.
Centralized guidance on planning:
Is there centralized guidance/support for government agencies on the preparation and costing of climate-aware public investment strategies?
C.2.a.
Coordination across central government:
Is decision making on public investment coordinated across central government from a climate-change perspective?
C.2.b.
Coordination with subnational governments:
Is the planning and implementation of capital spending of sub-national governments coordinated with the central government from a climate-change perspective?
C.2.c.
Oversight framework for PCs:
Does the regulatory and oversight framework for public corporations ensure that their climate-related investments are consistent with national climate policies and guidelines
C.3.a.
Climate analysis in project appraisal:
Does the appraisal of major infrastructure projects require climate-related analysis to be conducted according to a standard methodology with central support?
C.3.b.
PPP framework including climate risks:
Does the framework for managing longer-term public investment contracts, such as PPPs, explicitly address climate-related challenge?
C.3.c.
Climate consideration in project selection:
Are climate-related elements included among the criteria used by the government for the selection of infrastructure projects?
C.4.a.
Climate budget tagging:
Are planned climate-related public investment expenditures, sources of financing, outputs and outcomes identified in the budget and related documents, monitored, and reported?
C.4.b.
Ex post review of projects:
Are ex-post reviews or audits conducted of climate change mitigation and adaptation outcomes of public investments?
C.4.b.
Asset management:
Are ex-post reviews or audits conducted of climate change mitigation and adaptation outcomes of public investments?
C.5.a.
Disaster risk management strategy:
Does the government publish a national disaster risk management strategy that incorporates the projected impact of climate change on public infrastructure assets and networks?
C.5.b.
Ex ante financing mechanisms:
Has the government put in place ex-ante financing mechanisms to manage the exposure of the stock of public infrastructure to climate-related risks?
C.5.c.
Fiscal risk analysis including climate risk:
Does the government conduct and publish a fiscal risk analysis that incorporates climate-related risks to public infrastructure assets?
 |
Cross-Cutting Institutions Legal Framework, IT System, Staff Capacity |
 |
1. C-PIMA is a diagnostic tool to assess institutional readiness and gaps in infrastructure governance against the backdrop of climate change challenges in countries of all capacity levels.
2. It formulates a set of tailored recommendations and a prioritized and sequenced action plan that will support the implementation of the most appropriate infrastructure projects for the country.
3. It also can facilitate access to climate finance through helping countries improve their infrastructure governance.
4. The findings of a C-PIMA are summarized in a concise report, which also discusses the linkages between climate change, public infrastructure and climate strategies in a country.
Scoring
The C-PIMA is designed around five pillars of public investment management that are key for climate-aware infrastructure: planning, coordination across government, project appraisal and selection, budgeting and portfolio management, and risk management. Each institution is analyzed along three dimensions that reflect the key features of the given institution, resulting in a total of 15 dimensions. Three possible scores are assigned to each dimension (1: not met, 2: partially met, 3: fully met) and their average produces a score for that institution. C-PIMA scores are summarized in a chart that allows comparison with its comparators. In the chart, the further away from the center, the higher the C-PIMA scores. |
||||
Note: Country borders or names do not necessarily reflect the IMF’s official position.
⚠ Some users may experience reduced functionality using Internet Explorer. For the optimal experience, use Chrome or another alternative browser.